Linux without the hassle of partitioning. How to do it? Here is the answer. You can uninstall whenever you want!
Wednesday, April 27, 2016
Thursday, December 17, 2015
How to install Linux on Pendrive using F2FS Filesystem
Well, F2FS filesystem is specially designed by Samsung which is good for SSDs and pendrives. It makes the read and write operations on the devices much faster, because it is specially designed for those mediums. Even take a look at these benchmarks to prove that F2FS performance is better.
Monday, June 8, 2015
At last I can access Recovery Mode in Symphony GoFox F15! (with video)
As I blogged earlier, I got myself a Symphony GoFox F15 phone which runs the darling of open source, Firefox OS. This phone is now very cheap, new at BDT 2000. Insane, right? If you are a young passionate developer, now is the right time to buy it, and mingle with this amazing creation.
Tuesday, May 19, 2015
Saturday, January 24, 2015
Success! Symphony Gofox F15 ADB connection working under Ubuntu!
Recently I bought a Symphony Gofox F15 Firefox OS phone that is available in Bangladesh for $60 (4650 BDT). I bought a used one from bikroy.com with 3100 BDT. It is not a very appreciable set in terms of performance but it works. It is a Firefox OS 1.4 phone having 512mb RAM & ROM that gets a bit slow on heavy usage.
As a Web Developer myself I am thrilled that an entire mobile phone can be operated from browsers. If you are new to the trend, everything you see on FFOS is running on browsers, every button that you click is a <a> or <button> tag, every image that you see is either CSS or an <img> tag. So the OS takes very less RAM and resources to run, on theory.
But I must admit, some features are very well thought and they are way ahead compared to some earlier versions of Android. The 2.0 version also comes with a brilliantly designed UI that'll impress you for sure.
The good fun in ADB connection is the fact that you can run the app, debug it, touch different elements and inspect it in real time from your desktop PC! You can even modify styles of app drawer in an instant and with only changing some good old CSS codes.
As you expect, as it is less used in Bangladesh, I couldn't find the appropriate drivers for the phone's ADB connection. Although Mass storage worked right out of the box. The conclusion is, in Windows (both 32 & 64 bit) I failed to load it in WebIDE. But I succeeded in Ubuntu. Here's how I did it:
First ran the command on terminal:
2. Now run:
Earlier versions are less likely to work. It is best to get the latest possible version.
Get the Firefox tar file, extract it in a directory like this:
2. Installed the ADB Helper
from here: https://ftp.mozilla.org/pub/mozilla.org/labs/fxos-simulator/
2. Disabled Screen Lock from Settings -> Screen Lock (Because if the screen lock comes, the debug bridge will be stopped.)
3. Most importantly, enabled Developer menu, Settings -> Device Information -> More Information and checked "Developer Menu". A Developer item is now revealed in the Settings.
Then enabled ADB option from Settings -> Developer -> Remote Debugging -> ADB and Devtools.
1. Found a good cable from another phone and conneted with it. The cable given in the box does not work. Also sometimes, I heard, using a USB port directly on the motherboard helps. But I used extension cord and still got connection. I was lucky!
2. Started Firefox Nightly (from home/Apps/firefox) and opened about:app-manager through the addressbar. It showed a button with a strange number at the bottom. I clicked on it. It showed some errors, like this:
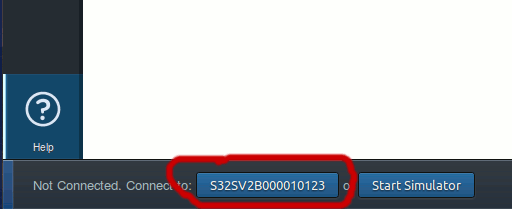
3. Out of curiosity I ignored the message and then tried opening the WebIDE (from Firefox menu -> Developer -> WebIDE.) and it showed the device in the Menu on the right side! This time it also showed the strange number, not exactly the device name (S32SV2B000010123). But I clicked on it anyway.
(After requesting connection with the device, there will be a message in your phone asking whether you want your Desktop to connect with your phone. Tap on OK button on your phone when it comes.)
Surprisingly, it connected!
4. I disabled and re-enabled ADB from Settings, started Firefox Nightly, plugged in the phone, started WebIDE and voila! It came with the right name!
Here goes a screenshot to my success!
2. Use a good quality cable
3. Connect it directly in the USB port of motherboard
4. Try enabling and disabling ADB option if doesn't get detected
5. Use this page to troubleshoot .
Anytime I wanted to connect, I just followed the point 4 under step 4.
Now I can create Apps in my Firefox browser and run it directly on my phone! yayy!
Help & ref:
https://bugzilla.mozilla.org/show_bug.cgi?id=936909
https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Tools/WebIDE/Troubleshooting
As a Web Developer myself I am thrilled that an entire mobile phone can be operated from browsers. If you are new to the trend, everything you see on FFOS is running on browsers, every button that you click is a <a> or <button> tag, every image that you see is either CSS or an <img> tag. So the OS takes very less RAM and resources to run, on theory.
But I must admit, some features are very well thought and they are way ahead compared to some earlier versions of Android. The 2.0 version also comes with a brilliantly designed UI that'll impress you for sure.
The good fun in ADB connection is the fact that you can run the app, debug it, touch different elements and inspect it in real time from your desktop PC! You can even modify styles of app drawer in an instant and with only changing some good old CSS codes.
As you expect, as it is less used in Bangladesh, I couldn't find the appropriate drivers for the phone's ADB connection. Although Mass storage worked right out of the box. The conclusion is, in Windows (both 32 & 64 bit) I failed to load it in WebIDE. But I succeeded in Ubuntu. Here's how I did it:
Connecting Gofox F15 for ADB/WebIDE in Ubuntu:
Step 1: Prepping the Ubuntu:
1. Created an udev rule for the device.First ran the command on terminal:
sudo gedit /etc/udev/rules.d/51-android.rulesThen added the following code in the file and saved:
SUBSYSTEM=="usb", ATTRS{idVendor}=="1782", MODE="0666"(I got the 1782 value from running lsusb command.)
2. Now run:
sudo service udev restart
Step 2: Prepping Firefox Desktop:
1. Got the latest Firefox Nightly for Linux (currently version 38) from hereEarlier versions are less likely to work. It is best to get the latest possible version.
Get the Firefox tar file, extract it in a directory like this:
cd ~(I have created and chosen the "Apps" directory. You can use any directory you want.)
mkdir Apps
cd Apps
tar xvf 'path/to/firefox-xxx.tar'
2. Installed the ADB Helper
from here: https://ftp.mozilla.org/pub/mozilla.org/labs/fxos-simulator/
Step 3: Prepping the Phone:
1. Turned on the USB Storage option from Settings2. Disabled Screen Lock from Settings -> Screen Lock (Because if the screen lock comes, the debug bridge will be stopped.)
3. Most importantly, enabled Developer menu, Settings -> Device Information -> More Information and checked "Developer Menu". A Developer item is now revealed in the Settings.
Then enabled ADB option from Settings -> Developer -> Remote Debugging -> ADB and Devtools.
Step 4: Bridging the ADB:
1. Found a good cable from another phone and conneted with it. The cable given in the box does not work. Also sometimes, I heard, using a USB port directly on the motherboard helps. But I used extension cord and still got connection. I was lucky!
2. Started Firefox Nightly (from home/Apps/firefox) and opened about:app-manager through the addressbar. It showed a button with a strange number at the bottom. I clicked on it. It showed some errors, like this:
12:34:56: connection error. Possible causes: USB port not connected, port not forwarded (adb forward), wrong host or port, remote debugging not enabled on the device.
3. Out of curiosity I ignored the message and then tried opening the WebIDE (from Firefox menu -> Developer -> WebIDE.) and it showed the device in the Menu on the right side! This time it also showed the strange number, not exactly the device name (S32SV2B000010123). But I clicked on it anyway.
(After requesting connection with the device, there will be a message in your phone asking whether you want your Desktop to connect with your phone. Tap on OK button on your phone when it comes.)
Surprisingly, it connected!
4. I disabled and re-enabled ADB from Settings, started Firefox Nightly, plugged in the phone, started WebIDE and voila! It came with the right name!
Here goes a screenshot to my success!
Remarks:
1. Use shorter cable if possible2. Use a good quality cable
3. Connect it directly in the USB port of motherboard
4. Try enabling and disabling ADB option if doesn't get detected
5. Use this page to troubleshoot .
Anytime I wanted to connect, I just followed the point 4 under step 4.
Now I can create Apps in my Firefox browser and run it directly on my phone! yayy!
Help & ref:
https://bugzilla.mozilla.org/show_bug.cgi?id=936909
https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Tools/WebIDE/Troubleshooting
Monday, January 5, 2015
Notepad++ - how to run a python script quickly
I was making a mp3 player python script the other day and I had to use IDLE for the advantage of running the script.In IDLE you have a nifty keyboard shortcut F5 to run the script immediately. There is nothing wrong with it until I found out some commenting shortcuts that I don't like and some features that I miss from my favorite text editor Notepad++.
I was searching for a solution how to have a run feature just like the Python IDLE so that I can use Notepad++ for my purpose. I found some solutions but none of them worked for my purpose perfectly.
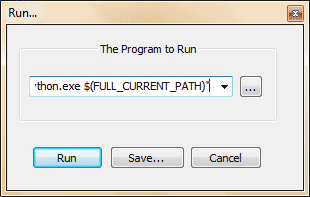
I tried NPP Exec plugin, and some other solutions but this one worked best for me.
2. Copy and Paste the following:
After that you can just press enter to run the script. But we want to save our command for later use. And we would also add a keyboard shortcut to that command.
3. Then click "Save..."
4. I have named my command "Run Python script"
5. I have assigned a Ctrl+F5 keyboard shortcut to run the current script. But you can choose whatever is convenient to you.
And don't forget to save the file before pressing Ctrl+F5.
So everytime you have to run a python script, just press Ctrl+F5. Good luck.
I was searching for a solution how to have a run feature just like the Python IDLE so that I can use Notepad++ for my purpose. I found some solutions but none of them worked for my purpose perfectly.
I tried NPP Exec plugin, and some other solutions but this one worked best for me.
Solution
1. Press F5.2. Copy and Paste the following:
After that you can just press enter to run the script. But we want to save our command for later use. And we would also add a keyboard shortcut to that command.
3. Then click "Save..."
4. I have named my command "Run Python script"
5. I have assigned a Ctrl+F5 keyboard shortcut to run the current script. But you can choose whatever is convenient to you.
And don't forget to save the file before pressing Ctrl+F5.
So everytime you have to run a python script, just press Ctrl+F5. Good luck.
Tuesday, December 2, 2014
How to use SVN client with GitHub
I am used to SVN (SubVersioN) rather than git. I kind of hate git, maybe because its command line is harder for my brain to digest. Hopefully, GitHub supports both git and svn.
If you are like me you would be interested in using SVN with github repositories. In this post we are going to learn how to do just that.
1. In windows, run cmd. In Ubuntu/Linux, start the terminal (Don't ask me how. If you are using linux you're probably smart enough to figure this out yourself!)
2. Now type svn --help and then press enter. If you see usage instructions you have svn installed. Now skip to the next part.
If you don't have SVN installed,
On Windows, install Win32SVN. You may have to restart after installation.
On Ubuntu, run: sudo apt-get install subversion
On other linux distro except Ubuntu/Debian, refer to your package manager documentation to install subversion.
https://github.com/{user name}/{repo name}
Let's say we will be working with:
https://github.com/adnan360/cvstatichtml
1. Now go to the repo link with your browser (go to the above link if you don't have one). You will find an url under the title "HTTPS clone URL". Click Subversion to get an URL for SVN. Copy that url. [The url is usually like: https://github.com/{user name}/{repo name} Although you could use the github page link above but I showed that if you forget which url to use. ]
2. Now open command prompt or terminal. cd to a proper directory.
In Windows, you can use a shortcut to cd to a directory. Just open a directory in explorer, hold down Ctrl+Shift and right click, then select "Open terminal window here".
Don't worry about creating a directory. A directory with the name of the repo will be created.
3. Type svn co followed by a space. Then right click and select paste. Example:
It will take some time to download the repo.
4. Now cd to the repo directory. Example:
(We will need this cd command for executing later commands.)
5. Now run:
The commands above will prepare you to modify the code.
1. Create a branch:
Replace /my_awesome_update to something more personal to you. "Added a new branch" is just a message to identify this change to the repo (that you just made a branch). This will later help you to merge.
The trunk directory contains the downloaded code which is untouched. We copy the untouched code to branches/my_awesome_update. We would edit the code under that directory.
2. Now go to you {repo directory}/branches/my_awesome_update and make your changes.
1. Let's see the file status:
This will say which files were changed.
2. If you see a Question Mark (?) beside some files (in the svn status output), then add these files (or directories) to the repo with:
This is a bit boring sometimes but cool once you've done it.
Now check again with an svn status to see if you got any ? marks still. If you get any, use avn add "xxx" to add them.
3. Send changes:
Replace "My awesome new update" with your own description of the change.
Now you have it! You can submit your code to github! With SVN! How cool is that!
Ref: https://help.github.com/articles/support-for-subversion-clients/
EDIT: SVN URL fixed
If you are like me you would be interested in using SVN with github repositories. In this post we are going to learn how to do just that.
Got Client?
Make sure you have svn client installed. I am comfortable with svn command line. In windows I use Win32SVN which lets me use svn commands directly in the command prompt.1. In windows, run cmd. In Ubuntu/Linux, start the terminal (Don't ask me how. If you are using linux you're probably smart enough to figure this out yourself!)
2. Now type svn --help and then press enter. If you see usage instructions you have svn installed. Now skip to the next part.
If you don't have SVN installed,
On Windows, install Win32SVN. You may have to restart after installation.
On Ubuntu, run: sudo apt-get install subversion
On other linux distro except Ubuntu/Debian, refer to your package manager documentation to install subversion.
How to Checkout (Download files from a repo)
In the world of version control, Checkout is a fancy way of saying download a copy of the current repository (or repo). Each project is kept under a repository. Repo link for its page on github follows this format:https://github.com/{user name}/{repo name}
Let's say we will be working with:
https://github.com/adnan360/cvstatichtml
1. Now go to the repo link with your browser (go to the above link if you don't have one). You will find an url under the title "HTTPS clone URL". Click Subversion to get an URL for SVN. Copy that url. [The url is usually like: https://github.com/{user name}/{repo name} Although you could use the github page link above but I showed that if you forget which url to use. ]
2. Now open command prompt or terminal. cd to a proper directory.
In Windows, you can use a shortcut to cd to a directory. Just open a directory in explorer, hold down Ctrl+Shift and right click, then select "Open terminal window here".
Don't worry about creating a directory. A directory with the name of the repo will be created.
3. Type svn co followed by a space. Then right click and select paste. Example:
# svn co --depth empty https://github.com/adnan360/cvstatichtml
It will take some time to download the repo.
4. Now cd to the repo directory. Example:
# cd cvstatichtml
(We will need this cd command for executing later commands.)
5. Now run:
# svn up trunk # svn up --depth empty branches
The commands above will prepare you to modify the code.
How to modify code
In github, it is extremely recommended that you create a copy of the code in a separate directory then modify it. We copy the whole code in a "branch" then edit it. This way the original code is left untouched and safe from our goofy coding!1. Create a branch:
# svn up trunk # svn copy trunk branches/my_awesome_update # svn commit -m "Added a new branch"
Replace /my_awesome_update to something more personal to you. "Added a new branch" is just a message to identify this change to the repo (that you just made a branch). This will later help you to merge.
The trunk directory contains the downloaded code which is untouched. We copy the untouched code to branches/my_awesome_update. We would edit the code under that directory.
2. Now go to you {repo directory}/branches/my_awesome_update and make your changes.
How to send your code to GitHub (Yaaayy!)
If you've followed previous steps correctly, now its easy to send your update to github.1. Let's see the file status:
# svn status
This will say which files were changed.
2. If you see a Question Mark (?) beside some files (in the svn status output), then add these files (or directories) to the repo with:
# svn add {file or directory}
This is a bit boring sometimes but cool once you've done it.
Now check again with an svn status to see if you got any ? marks still. If you get any, use avn add "xxx" to add them.
3. Send changes:
# svn commit -m "My awesome new update"
Replace "My awesome new update" with your own description of the change.
Now you have it! You can submit your code to github! With SVN! How cool is that!
Ref: https://help.github.com/articles/support-for-subversion-clients/
EDIT: SVN URL fixed
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)